TECHNOLOGY
What is an IC Chips Used For, and Why It is Important
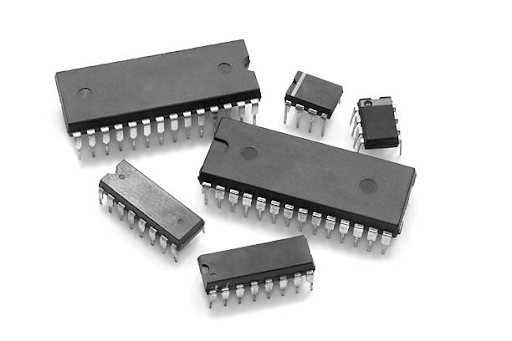
What is an IC Chip?
An Integrated Circuit( IC) chip, frequently called an IC, is a small electronic device comprising miniaturized electronic components similar to transistors, resistors, and capacitors. These components are etched onto a small semiconductor material, generally silicon, to perform specific functions.
IC chips are revolutionary because they can pack numerous components into a bitsy space, drastically perfecting the performance and effectiveness of electronic devices.
IC chips are the smarts behind nearly every electronic device you use. They perform various functions, from introductory calculations to complex signal processing, making them necessary in today’s tech-driven world.
The capability to integrate multiple functions into a single chip has paved the way for lower, more important, and more effective electronic devices. Choosing the right IC chip suppliers is essential for your tech projects.
The Evolution of IC Chips
The history of IC chips dates back to the late 1950s when Jack Kilby at Texas Instruments constructed the first intertwined circuit. This advance drastically reduced the size and cost of electronic devices.
Technological Advancements
Over the decades, IC technology has advanced exponentially. The preface of CMOS( reciprocal Metal—Oxide—Semiconductor) technology allowed for lower power consumption and advanced viscosity circuits. Moment, IC chips are fabricated using nanometer-scale processes, allowing billions of transistors to be placed on a single chip, as seen in ultramodern processors.
Impact on the Electronics Industry
The evolution of IC chips has revolutionized the electronics industry. It has enabled the development of compact, powerful, and affordable electronic devices. IC chips have driven this transformation from early computers occupying entire rooms to today’s smartphones fitting in your pocket.
How Do IC Chips Work?
IC chips are fabricated onto semiconductor wafers using photolithography and other advanced techniques. They consist of interconnected transistors, resistors, capacitors, and other electronic components.
Functioning in Electronic Circuits
IC chips manipulate electrical signals to perform their designated tasks at the core. For instance, in a simple digital IC, transistors act as switches that can turn on or off, representing the binary 1s and 0s fundamental to computer processing. In analog ICs, components like resistors and capacitors modulate the amplitude of continuous signals.
Examples of Specific IC Chips
Consider the microcontroller, an IC chip used extensively in embedded systems. It combines a single chip’s processor, memory, and input/output peripherals. Another example is the Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp), widely used in signal conditioning, filtering, and other applications requiring precise analog computations.
Types of IC Chips
Microprocessors
Microprocessors are the most well-known type of IC chip. These chips are the smarts of computers and other digital devices, executing instructions and calculating at inconceivable speeds. Microprocessors are in everything from desktop computers to smartphones and household appliances.
In this case, your computer’s CPU( Central Processing Unit) is a microprocessor. It handles tasks like running applications, managing system resources, and executing commands. Without microprocessors, ultramodern computing as we know it would not exist.
Memory Chips
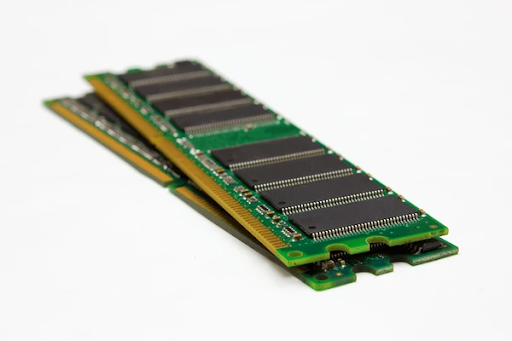
Memory chips are another pivotal type of IC chip. They store data and instructions that microprocessors need to execute tasks. There are several types of memory chips, including RAM( Random Access Memory), ROM(Read-Only Memory), and flash memory.
RAM is used as a temporary data storehouse while a device is powered on, allowing for quick access and manipulation of information. On the other hand, ROM stores endless data that does not change, similar to firmware. Flash memory, generally set up in USB drives and SSDs(Solid-State Drives), provides a non-volatile storehouse that retains data even when powered off.
Analog ICs
Analog ICs process nonstop signals, making them essential for audio modification, modulation, and detector interfacing applications. Unlike digital ICs, which work with double data, analog ICs handle real-world signals that vary continuously.
One typical illustration of an analog IC is the functional amplifier(op-amp). Op-amps are used in various applications, from audio outfits to medical devices. They can amplify small signals, making them useful for tasks like converting detector data into readable form.
Digital ICs
Digital ICs work with double data, performing logical operations and processing digital signals. These chips are the foundation of digital electronics, enabling data processing, communication, and control.
Digital ICs include sense gates, flip-duds, and counters. These components are used in various digital circuits and systems, such as computer processors, digital watches, and communication devices. Digital ICs are essential for creating complex electronic systems that perform intricate tasks.
What Is an IC Chip Used For?
Integrated Circuit (IC) chips are the tiny powerhouses behind our daily technology. Understanding the types of IC chips is one thing, but seeing how they’re applied in real-world devices can give a fuller picture. Then, examples of how each IC chip is utilized are provided.
Microprocessors in Smartphones
Smartphones are perfect exemplifications of devices powered by microprocessors. A smartphone’s central processing unit( CPU) is a microprocessor that handles everything from running apps to connecting to the Internet. Companies like Apple and Qualcomm design advanced microprocessors for mobile devices, optimizing them for performance and energy effectiveness.
Memory Chips in Computers
Computers calculate heavily on various types of memory chips. RAM is stored temporarily while the computer runs, ensuring smooth operation and quick access to information. On the other hand, Flash memory is used in solid-state drives( SSDs) for long-term data storage, offering faster read and write speeds than traditional hard drives.
Analog ICs in Audio Equipment
A high-dedication audio outfit uses analog ICs to reuse sound signals. Functional amplifiers, for example, amplify audio signals to drive speakers and headphones. Analog-to-digital transformers convert analog audio signals into digital form for processing and storage, ensuring high-quality sound reproduction.
Digital ICs in Embedded Systems
Embedded systems, such as those in smart home devices and industrial automation, use digital ICs extensively. Microcontrollers, a digital IC, integrate a CPU, memory, and input/output peripherals on a single chip, enabling efficient control and communication within these systems.
Why Are IC Chips Important?
Efficiency and Miniaturization
One of the most significant advantages of IC chips is their capability to perform complex tasks efficiently while occupying minimum space. This miniaturization has led to the development of compact and movable devices, making technology more accessible for everyday use. For example, the miniaturization enabled by IC chips has made laptops lighter and, more importantly, transformed how we work and play.
Reliability and Performance
IC chips are known for their trustability and high performance. They can operate under various conditions, making them suitable for multiple applications, from consumer electronics to industrial machinery. Their robustness ensures that devices serve quickly and constantly, reducing the liability of failures and conservation issues. In industrial settings, IC chips are used in automation systems to enhance productivity and perfection.
Enabling Innovation
The versatility of IC chips fosters invention across multiple industries. Engineers and designers can integrate these chips into new products and systems, pushing the possible boundaries. Whether developing cutting-edge AI applications or creating smart home devices, IC chips are at the forefront of technological advancements. In artificial intelligence, for example, IC chips power machine-learning algorithms that drive inventions like natural language processing and computer vision.
Applications of IC Chips
IC chips are set up in nearly every electronic device imaginable, from smartphones and computers to buses and satellites. Without them, ultramodern technology as we know it would not exist. Then are some common uses of IC chips
Consumer Electronics
IC chips are the heart of consumer electronics. From smartphones and tablets to smartwatches and gaming consoles, these chips handle pivotal tasks like recycling data, managing power, and enabling wireless communication. For example, your smartphone’s CPU( central processing unit) is an IC chip that performs billions of computations per second to run apps, display graphics, and connect to the Internet.
Automotive Industry
Modern vehicles are becoming increasingly reliant on IC chips. These chips control everything from machine management and energy injection to advanced driver-assistance systems( ADAS) and in-auto entertainment. The rise of electric vehicles( EVs) has further amplified the significance of IC chips, as they manage battery performance, regenerative retardation, and independent driving features.
Medical Devices
IC chips play a vital part in healthcare technology. They’re used in various medical devices, such as leaders, MRI machines, and movable individual tools. These chips ensure precise control and dependable performance, which are critical for patient safety and effective treatment. For example, an IC chip in a pacemaker regulates the heart’s meter by transferring electrical impulses.
The Future of IC Chips
The future of IC chips looks incredibly promising, with several innovative trends and inventions on the horizon. One of the most significant developments is the rise of artificial intelligence( AI) and machine learning. AI-specific IC chips, known as AI accelerators, are designed to handle the massive computational demands of AI applications, offering unknown performance and effectiveness.
Another exciting trend is the development of quantum computing. Quantum IC chips use the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations at orders of magnitude faster than traditional silicon-ground chips. While still experimental, quantum IC chips can potentially revise fields such as cryptography, medicine discovery, and climate modeling.
Flexible and wearable electronics represent another frontier for IC technology. Experimenters are developing IC chips that can bend, stretch, and conform to various surfaces, opening up new possibilities for applications in healthcare, wearable devices, and intelligent textiles. These inventions promise to integrate technology into our daily lives, offering new convenience and functionality.
Conclusion
IC chips are the tiny powerhouse driving ultramodern technology, enabling the devices and systems we rely on daily. From their humble onsets to their current state of complication, IC chips have come a long way, continually pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
Their significance can not be overstated, as they are pivotal in perfecting effectiveness, enhancing performance, and driving invention across various industries. Understanding IC chips is essential for tech enthusiasts, electronics hobbyists, and IT professionals to appreciate the inner workings of modern technology.
Whether building a robot, developing software, or simply tinkering with electronics, choosing the right IC chip suppliers is crucial for achieving optimal performance and efficiency.
TECHNOLOGY
Unlocking the Power of Plangud: A Comprehensive Guide

Enter Plangud a revolutionary tool designed to streamline your planning and productivity like never before. Whether you’re an entrepreneur juggling multiple projects or a student managing assignments, Plangud offers a unique approach to organization that can transform how you work.
Imagine having all your tasks, deadlines, and goals in one place. Picture a system that not only helps you plan but also motivates you to achieve more each day. This is the power of Plangud. It combines simplicity with functionality, making it accessible for anyone who wants to enhance their workflow.
Curious about what makes this platform so special? Let’s dive deeper into the world of Plangud and explore how it can revolutionize your daily routine and boost your productivity!
The Benefits of Using Plangud
Plangud offers a range of benefits that can transform how you approach tasks. Its intuitive interface makes it easy for anyone to navigate and utilize effectively. This simplicity encourages more users to adopt the platform seamlessly.
One major advantage is its ability to enhance collaboration among team members. Everyone stays on the same page, reducing misunderstandings and boosting productivity. Real-time updates ensure that changes are visible instantly, fostering a sense of teamwork.
Additionally, Plangud promotes better time management through its scheduling features. Users can prioritize tasks efficiently, ensuring deadlines are met without unnecessary stress.
Moreover, the analytics tools provide valuable insights into progress and performance metrics. These data-driven reports help identify areas for improvement and streamline workflows further.
Using Plangud ultimately leads to increased efficiency in both individual and group projects. The platform’s versatility caters to diverse needs across various industries.
How to Get Started with Plangud
Getting started with Plangud is easy and straightforward. First, visit the official website to create an account. Registration typically requires just a few basic details.
Once you’re signed up, take some time to explore the platform’s features. Familiarize yourself with its user interface and tools designed for planning and organization.
Next, set your goals. Define what you want to achieve using Plangud—whether it’s managing projects or personal tasks.
Consider integrating existing data or materials into your new workspace. This can save time and help streamline your workflow from the get-go.
Don’t hesitate to check out tutorials or guides within the platform. These resources provide valuable insights that can enhance your experience right away.
Start small by creating simple plans before diving into more complex projects. Build confidence gradually while adapting Plangud to fit your unique needs.
Tips for Maximizing Productivity with Plangud
To truly harness the power of Plangud, start by setting clear and achievable goals. Break larger tasks into smaller steps to maintain focus and momentum.
Utilize the scheduling feature effectively. Block out specific times for different projects. This helps create a structured workflow that prevents distractions.
Leverage collaboration tools within Plangud. Engage with your team by sharing ideas or progress updates in real time. Communication is crucial for maintaining productivity.
Incorporate regular check-ins with yourself or your team to assess what’s working and what isn’t. Adjustments may be necessary along the way.
Familiarize yourself with keyboard shortcuts available in Plangud. They can significantly speed up navigation, allowing you more time for actual work rather than clicking around aimlessly.
Integrating Plangud into Your Daily Routine
Integrating Plangud into your daily routine can transform how you manage tasks. Start by setting aside a few minutes each morning to outline your day using the platform. This helps prioritize important activities.
Consider syncing Plangud with other tools you already use. Whether it’s email or calendar apps, integration streamlines processes and keeps everything in one place.
During work hours, take advantage of reminders for deadlines and meetings. This feature ensures that nothing slips through the cracks while keeping you focused on what matters most.
Make it a habit to review your progress at the end of each day. Reflecting on accomplishments fosters motivation and identifies areas for improvement.
Encourage colleagues or team members to adopt Plangud as well. A shared approach enhances collaboration and accountability within projects.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Plangud in Various Industries
Plangud has made waves across various industries by enhancing workflow and productivity. In the tech sector, a leading software company adopted Plangud to streamline project management. The result? A 30% reduction in time spent on task allocation.
In healthcare, a hospital integrated Plangud for scheduling staff shifts. This shift led to improved patient care through better resource management, allowing nurses and doctors to focus on what truly matters—patient well-being.
Retail businesses have also reaped benefits. One prominent chain utilized Plangud for inventory tracking and supply chain coordination. They experienced significant cost savings and minimized stockouts that often frustrated customers.
Even educational institutions embraced this tool. A university used Plangud to coordinate course offerings, resulting in higher student satisfaction rates due to streamlined class schedules and resources.
These examples showcase how versatile Plangud can be when tailored effectively across different fields.
Common Challenges and Solutions When Using Plangud
Using Plangud can transform productivity, but it’s not without its challenges. One common hurdle is user resistance. Many people hesitate to adopt new tools, fearing disruption in their workflow.
Training sessions and onboarding tutorials can help ease this transition. Comprehensive resources empower users to explore Plangud’s features confidently.
Another issue is integration with existing systems. Smooth functionality depends on seamless collaboration among various tools. It’s crucial to invest time in setting up integrations properly.
Technical glitches or bugs may arise during implementation as well. Regular updates from the developers often address these issues promptly, so staying informed about upgrades is essential.
Some users struggle with overwhelmed project views due to excessive task details. Customizing dashboards allows individuals to focus on what matters most while reducing visual clutter for increased clarity and efficiency.
Conclusion
Plangud has emerged as a powerful tool for individuals and businesses alike. Its versatility allows users to tailor their planning and productivity strategies effectively. By understanding how Plangud works, you open the door to numerous benefits that can transform your daily operations.
Getting started is straightforward, making it accessible even for those who may not consider themselves tech-savvy. With some initial setup and exploration of its features, users can begin reaping the rewards of enhanced organization and efficiency.
Maximizing productivity with Plangud involves integrating its various functionalities into your workflow seamlessly. Utilizing tips like setting specific goals or utilizing reminders can elevate your experience further. As you incorporate Plangud into your daily routine, you’ll find new ways to stay on track while minimizing stress.
TECHNOLOGY
Infector virus: How They Spread and Impact Our Lives
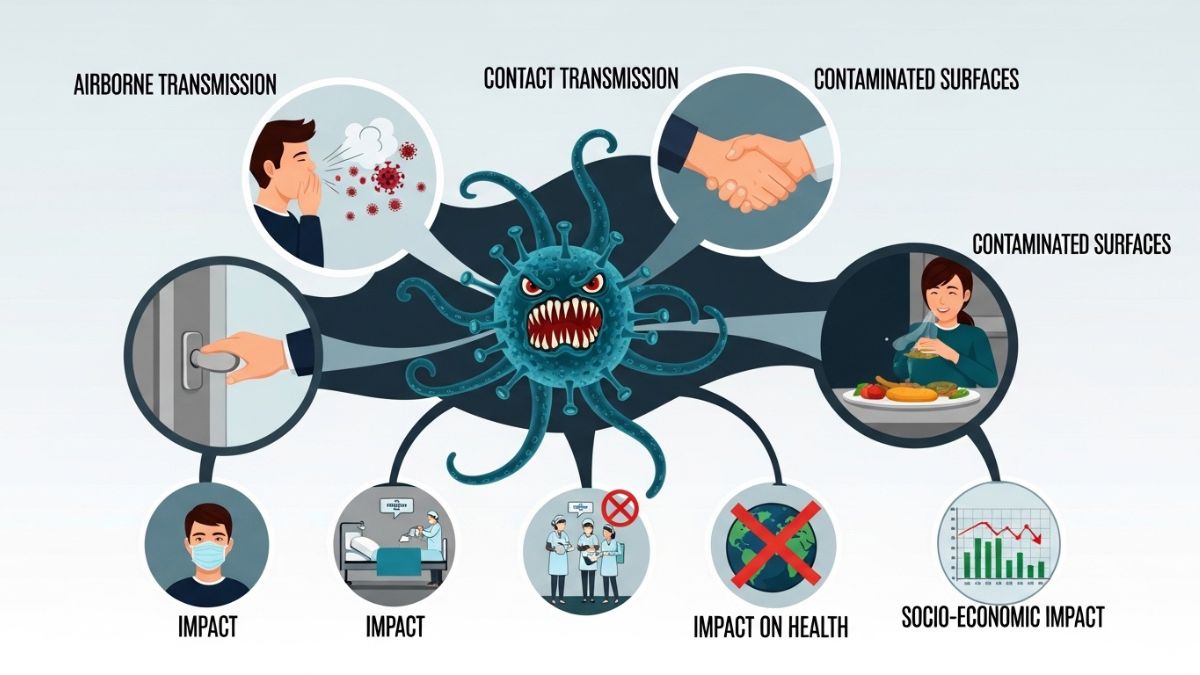
Viruses are tiny entities that can have a massive impact on our lives. From the common cold to more severe illnesses, these microorganisms are everywhere. They can spread quickly and affect millions of people in a matter of days. Among them, infector viruses stand out due to their ability to invade host cells and replicate efficiently.
Understanding how these viruses operate is crucial in today’s world, where global travel and interconnectedness make outbreaks more likely than ever. As we dive into the specifics of infector viruses, we’ll uncover how they spread and why it matters for our health and safety. Join us as we explore this fascinating yet concerning aspect of microbiology that affects us all.
What is an infector virus?
An infector virus is a type of microorganism that can invade living cells. Once inside, it hijacks the cell’s machinery to replicate itself. This process often leads to cell damage or death.
These viruses come in various shapes and sizes. Some are simple, while others have complex structures with protective coatings. Their ability to adapt makes them particularly challenging for our immune systems.
Infector viruses can affect a wide range of organisms, from humans and animals to plants and bacteria. They play significant roles in ecosystems but can also cause serious health issues.
Understanding how these viruses operate helps researchers develop vaccines and treatments. The study of infector viruses is crucial for public health as we navigate emerging threats around the globe.
How do infector viruses spread?
Infector viruses can spread through various means, making them particularly challenging to control. One primary mode of transmission is direct contact. When an infected person touches another individual or a surface, the virus can transfer easily.
Airborne particles also play a significant role in spreading these viruses. As we breathe, talk, or cough, tiny droplets containing the virus become suspended in the air. Others may inhale these droplets without even realizing it.
Another common way infector viruses propagate is via contaminated surfaces and objects. Viruses can survive on doorknobs, phones, and utensils for hours or even days. Touching these surfaces and then touching your face increases the risk of infection dramatically.
Some infector viruses require vectors like insects to transmit between hosts. Mosquitoes are well-known carriers that facilitate this type of spread by biting an infected host and then transferring the virus to others they bite thereafter.
The effects of infector viruses on our health
Infector viruses can have profound effects on human health. They enter the body and exploit our cells for reproduction, often leading to illness. Symptoms may range from mild discomfort to severe conditions that require hospitalization.
Influenza is a prime example of an infector virus that causes seasonal outbreaks. It can lead to respiratory problems, fever, and fatigue. For vulnerable populations like the elderly or those with underlying health issues, these viruses pose even greater risks.
Moreover, some infector viruses can result in long-term health consequences. Conditions such as chronic fatigue syndrome or post-viral syndromes can linger well after initial infection has subsided.
The psychological impact shouldn’t be overlooked either; fear of viral outbreaks can contribute to anxiety and stress among communities. Awareness and understanding are crucial in navigating these challenges effectively.
Recent outbreaks of infector viruses
Recent outbreaks of infector viruses have captured global attention and concern. The rise in new strains has highlighted our vulnerability to these microscopic foes.
For instance, the emergence of novel coronaviruses has led to significant disruptions worldwide. Each outbreak brings about unique challenges in containment and response efforts.
Influenza variants also continue to circulate, reminding us that vigilance is necessary year-round. Health organizations are constantly monitoring changes in viral behavior and transmission rates.
In regions with dense populations, the spread can be rapid and devastating. Vaccination campaigns play a crucial role in mitigating risks during peak seasons.
Social distancing measures have become commonplace during such crises, but they come with economic costs as well. The interconnectedness of our world means that an outbreak anywhere can quickly turn into a global issue.
Efforts for better surveillance systems are underway to track these viruses more effectively, aiming for quicker responses when outbreaks occur.
How to protect against infector viruses
Staying vigilant is key when it comes to protecting yourself from infector viruses. Start with good hygiene practices. Frequent hand washing with soap for at least 20 seconds can significantly reduce your risk of infection.
Consider using hand sanitizer, especially in crowded places where soap and water aren’t available. Choose one that contains at least 60% alcohol for maximum effectiveness.
Vaccination plays a crucial role as well. Stay updated on recommended vaccines that protect against specific viruses prevalent in your area or traveling destination.
Avoid close contact with sick individuals whenever possible. Maintain a safe distance during outbreaks, and don’t hesitate to wear masks if advised by health authorities.
Keep informed about local health advisories and follow any guidelines provided by public health officials. Awareness helps you make better choices to stay healthy amidst potential threats from infector viruses.
Conclusion
Viruses are tiny entities that wield significant influence over our lives. Among them, infector viruses stand out due to their ability to cause illness and outbreaks. Understanding these viruses is crucial for safeguarding ourselves and our communities.
An infector virus is a type of pathogen known for its capacity to invade host cells, replicate, and spread throughout populations. They can be responsible for a broad spectrum of diseases, from mild infections like the common cold to more severe illnesses such as COVID-19 or influenza.
These viruses spread through various means—airborne transmission via respiratory droplets, direct contact with infected surfaces, or even through bodily fluids. Their adaptability allows them to find new hosts quickly and efficiently.
The impact on health can vary significantly depending on the specific virus in question. Symptoms might range from mild discomfort to severe illness requiring hospitalization. Vulnerable groups such as the elderly or those with pre-existing conditions often face heightened risks.
TECHNOLOGY
Exploring Ingebim: The Ultimate Guide to Understanding Its Impact

In a world driven by innovation, few concepts capture the imagination quite like Ingebim. This cutting-edge technology is changing how we think about data management and operational efficiency. As businesses continue to look for smarter solutions, understanding Ingebim has become essential. But what exactly is it? And how does it influence industries today?
From its humble beginnings to its current revolutionary applications, the journey of Ingebim is as fascinating as it is impactful. Whether you’re a business leader seeking competitive advantage or simply curious about technological advancements, this guide will take you through everything you need to know about Ingebim. Buckle up; we’re diving deep into the realm of possibilities!
What is Ingebim?
Ingebim is a powerful tool designed to streamline data integration and business intelligence processes. At its core, it serves as a bridge between various data sources, allowing organizations to gather insights with ease.
Think of Ingebim as the ultimate connector. It takes disparate systems and transforms them into cohesive platforms for analysis. This allows users to harness valuable information without grappling with complex coding or manual data entry.
The technology utilizes advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques that enhance decision-making efficiency. Its user-friendly interface enables even non-technical users to navigate the system effortlessly.
With Ingebim, businesses can automate tasks that once required substantial human effort. This leads not only to time savings but also improved accuracy in reporting and analytics. As more companies adopt this innovative solution, its significance continues to grow across industries worldwide.
The History and Evolution of Ingebim
Ingebim traces its roots back to the early digital landscape, where data management and analysis were burgeoning fields. Initially focused on basic databases, it evolved with technology’s rapid pace.
As businesses recognized the potential of big data, Ingebim adapted by integrating advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques. This transition marked a pivotal moment in its evolution, allowing for deeper insights and predictions based on vast datasets.
The 2010s witnessed an explosion in cloud computing. Ingebim capitalized on this shift by offering scalable solutions that catered to organizations of all sizes.
Today, it stands as a versatile tool that combines analytics with user-friendly interfaces. Its growth reflects ongoing innovations in data science and the increasing demand for intelligent decision-making tools across various industries.
How Ingebim Works
Ingebim operates through a sophisticated network of algorithms and data analysis techniques. At its core, it leverages machine learning to interpret vast amounts of information.
The system begins by collecting diverse data sets from various sources. This can include user behavior, environmental factors, or industry trends. Once gathered, the data undergoes rigorous processing and cleansing to ensure accuracy.
Next comes the analysis phase. Here, Ingebim uses predictive modeling to uncover patterns that might not be immediately obvious. It identifies correlations that can inform decision-making processes across different sectors.
Moreover, Ingebim’s adaptability allows it to adjust as new information becomes available. This continuous learning helps refine outcomes over time. Users benefit from real-time insights that drive strategic initiatives forward without delay.
Real-life Examples of Successful Ingebim Implementation
Companies across various industries have begun to harness the power of Ingebim, achieving remarkable results. One notable example is a retail giant that integrated Ingebim into its supply chain management. The technology streamlined operations, reducing delivery times and increasing customer satisfaction.
In the healthcare sector, a hospital network used Ingebim to enhance patient data management. This implementation improved communication among staff and led to faster diagnosis and treatment options for patients.
Another interesting case comes from finance. A fintech startup utilized Ingebim for fraud detection in real-time transactions. By analyzing patterns swiftly, the company minimized losses significantly while gaining consumer trust.
These examples illustrate how diverse sectors can leverage Ingebim’s capabilities, transforming challenges into opportunities for growth and innovation. Each success story adds to the growing narrative of what this technology can accomplish when applied thoughtfully.
The Benefits and Drawbacks of Using Ingebim
Ingebim offers numerous advantages that can significantly enhance operational efficiency. By streamlining processes, it helps organizations save time and reduce costs. Many users report improved data accuracy as well.
However, there are challenges to consider. Implementation can be complex, often requiring extensive training for staff. This learning curve may temporarily disrupt productivity.
Security is another concern. Storing sensitive information within Ingebim systems raises risks related to data breaches. Organizations must invest in robust cybersecurity measures to mitigate these threats.
Moreover, reliance on technology can lead to vulnerabilities if the system experiences downtime or fails unexpectedly. Balancing automation with human oversight becomes crucial in such scenarios.
Weighing these benefits against drawbacks is essential for companies considering Ingebim adoption. Understanding both sides will aid informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Ethical Concerns Surrounding Ingebim
The rise of Ingebim brings with it a host of ethical concerns. Privacy is at the forefront. As data collection becomes more sophisticated, individuals may unknowingly surrender their personal information.
There’s also the risk of bias in decision-making processes powered by Ingebim systems. If the underlying algorithms are flawed or trained on skewed data, outcomes could disproportionately affect certain groups.
Transparency is another significant issue. Many users lack a clear understanding of how Ingebim functions and how decisions are made based upon its analyses.
Moreover, accountability becomes murky when automated systems operate independently. Who takes responsibility for mistakes? The developers? The users?
As organizations increasingly adopt Ingebim technology, there looms an ethical dilemma around dependency on machines versus human judgment. Striking a balance between efficiency and moral considerations remains crucial as we navigate this evolving landscape.
Future Predictions for the Growth of Ingebim
As technology continues to advance, the growth of Ingebim appears promising. Experts forecast an increased adoption across various sectors, particularly in healthcare and finance. This trend is driven by a rising demand for efficient data management and analysis.
Furthermore, advancements in artificial intelligence could enhance Ingebim’s capabilities significantly. With machine learning integration, organizations may leverage real-time insights more effectively than ever before.
The global push for digital transformation also plays a crucial role. Companies are recognizing the need to streamline operations through innovative solutions like Ingebim.
Additionally, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve alongside technological progress. This will create both challenges and opportunities as industries adapt to new standards surrounding data usage.
Emerging markets might lead this charge too. As they invest in infrastructure, Ingebim’s reach can expand further into previously untapped regions.
Conclusion
As we delve into the complexities of Ingebim, it becomes clear that this innovative tool is reshaping industries across the board. Its unique functionalities offer organizations the chance to streamline processes and enhance efficiency. Understanding its history allows us to appreciate how far technology has come, paving the way for future advancements.
The real-life examples highlight just how transformative Ingebim can be when implemented successfully. However, it’s crucial to weigh both benefits and drawbacks carefully. The ethical concerns surrounding data privacy and security remind us of our responsibilities as users.
Looking ahead, predictions about Ingebim’s growth suggest an exciting trajectory filled with potential innovations. As businesses continue to adapt and integrate new technologies like Ingebim into their operations, staying informed will be essential for maximizing its advantages while navigating any associated challenges.
-

 HEALTH2 years ago
HEALTH2 years agoTransformative Health Solutions: Unveiling the Breakthroughs of 10x Health
-

 GENERAL2 years ago
GENERAL2 years agoDiscovering the Artistic Brilliance of Derpixon: A Deep Dive into their Animation and Illustration
-

 Posts2 years ago
Posts2 years agoSiegel, Cooper & Co.
-

 Lifestyle2 years ago
Lifestyle2 years agoPurenudism.com: Unveiling the Beauty of Naturist Lifestyle
-

 FASHION2 years ago
FASHION2 years agoThe Many Faces of “λιβαισ”: A Comprehensive Guide to its Symbolism in Different Cultures
-

 Lifestyle2 years ago
Lifestyle2 years agoBaddieHub: Unleashing Confidence and Style in the Ultimate Gathering Spot for the Baddie Lifestyle
-

 Entertainment2 years ago
Entertainment2 years agoGeekzilla Podcast: Navigating the World of Pop Culture, Gaming, and Tech
-

 Lifestyle2 years ago
Lifestyle2 years agoSandra orlow: Unraveling the Story of an Iconic Figure
